Lesbian, Gay, And Bisexual Youth: Navigating Mental Health Challenges
In this article, we will explore the unique mental health challenges faced by lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth. We will discuss how societal attitudes, discrimination, and lack of support can impact their well-being. By understanding the struggles they face, we can empower ourselves to create a more inclusive and supportive environment for all young individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation. Let’s take a compassionate journey to uncover the experiences of lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth and learn how we can be allies in their mental health journeys.
Understanding LGBTQ+ Identities
Exploring sexual orientation
Understanding LGBTQ+ identities begins with exploring sexual orientation. Sexual orientation refers to a person’s emotional, romantic, and sexual attractions to individuals of the same gender, different gender, or multiple genders. It is important to recognize that sexual orientation exists on a spectrum, and individuals may identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, pansexual, or other identities. By understanding and respecting different sexual orientations, we can create a more inclusive and accepting society.
Understanding gender identity
In addition to sexual orientation, gender identity is another important aspect of LGBTQ+ identities. Gender identity is a deeply-held sense of being male, female, or something beyond the binary construct of gender. Transgender individuals, for example, may have a gender identity that does not align with the sex assigned to them at birth. It is crucial to respect and affirm individuals’ gender identities, using their preferred pronouns and allowing them to express themselves authentically.
Differences between lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth
While lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth may all identify as part of the LGBTQ+ community, it is essential to acknowledge the unique experiences and challenges they face. Lesbian individuals are women who are attracted to other women, gay individuals are men who are attracted to other men, and bisexual individuals are attracted to both men and women. By recognizing the distinctions between these identities, we can better understand and support the diverse experiences of LGBTQ+ youth.
Mental Health Disparities
Impact of societal discrimination
Societal discrimination significantly impacts the mental health of LGBTQ+ youth. The stigma, prejudice, and discrimination they face can lead to feelings of shame, isolation, and low self-esteem. It is important to create a society that fosters acceptance and inclusivity to mitigate these negative effects.
Higher rates of mental health disorders
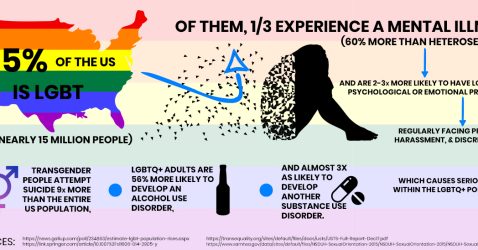
Research consistently shows that LGBTQ+ youth experience higher rates of mental health disorders compared to their heterosexual and cisgender peers. Anxiety, depression, substance abuse, and eating disorders are just a few of the mental health challenges they may face. These disparities emphasize the need for enhanced mental health support and resources specifically tailored to LGBTQ+ individuals.
Suicide rates and self-harm among LGBTQ+ youth
Tragically, LGBTQ+ youth are at a significantly higher risk of contemplating and attempting suicide compared to their heterosexual and cisgender counterparts. The internalized stigma, rejection from family and friends, and lack of acceptance contribute to their vulnerability. Moreover, rates of self-harm are also elevated among LGBTQ+ youth, highlighting the urgent need for accessible mental health services and supportive environments.
Coming Out Process
Challenges and fears of coming out
Coming out, the process of disclosing one’s LGBTQ+ identity to others, can be challenging and filled with numerous fears. LGBTQ+ youth may fear rejection, discrimination, and losing support from their loved ones. The fear of not being accepted for who they are often delays or complicates the coming out process. It is crucial to provide a supportive and safe environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their identities.
Supportive versus unsupportive reactions
The reactions LGBTQ+ individuals receive when they come out greatly impact their mental health and well-being. Supportive reactions, characterized by acceptance, love, and affirmation, contribute to positive mental health outcomes. Conversely, unsupportive reactions, such as rejection, discrimination, or attempts to change their sexual orientation or gender identity, can cause emotional distress and further isolate LGBTQ+ youth.
Navigating family dynamics
Coming out to family members can be particularly challenging for LGBTQ+ youth. Family support is crucial in promoting positive mental health outcomes and reducing the risk of negative mental health consequences. However, some families may struggle to understand or accept their child’s LGBTQ+ identity. It is essential to provide resources and guidance for families to navigate this process and foster healthy, supportive relationships within the family unit.
Intersectionality and LGBTQ+ Identities
Experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals with different racial or ethnic backgrounds
Intersectionality recognizes that individuals’ experiences are shaped by the intersection of multiple social identities. LGBTQ+ individuals from different racial or ethnic backgrounds may face unique challenges. For example, they may experience racism within the LGBTQ+ community or homophobia within their racial or ethnic community. Understanding the intersections of identities is crucial to creating an inclusive and supportive environment for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Unique challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals with disabilities
LGBTQ+ individuals with disabilities face a distinct set of challenges. They may encounter barriers to healthcare, face discrimination based on both their sexual orientation or gender identity and their disability status, and struggle with accessibility issues. It is important to address these unique challenges and ensure that LGBTQ+ individuals with disabilities have equal access to support and resources.
Understanding the impact of socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status plays a significant role in the experiences and mental health of LGBTQ+ individuals. Economic disparities, discrimination in the workplace, and limited access to resources create additional stressors for individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds. Recognizing the impact of socioeconomic factors is crucial in advocating for policies that address the specific needs and challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals in different economic circumstances.
Healthcare Disparities
Limited access to LGBTQ+-friendly healthcare
LGBTQ+ individuals often face barriers to accessing inclusive and affirming healthcare. Many healthcare providers lack training and knowledge on LGBTQ+ health issues, leading to a lack of understanding and appropriate care. Limited access to culturally competent healthcare services further exacerbates mental health disparities. Efforts must be made to expand LGBTQ+-friendly healthcare options and ensure that individuals can access the care they need without fear of judgment or discrimination.
Discomfort and lack of knowledge among healthcare providers
The discomfort and lack of knowledge among healthcare providers regarding LGBTQ+ issues create a significant barrier to quality healthcare. LGBTQ+ individuals may encounter judgment, misunderstanding, or even medical bias that can be detrimental to their well-being. It is imperative to prioritize ongoing education and training for healthcare providers to foster an inclusive and affirming healthcare environment.
The impact of healthcare disparities on mental health
Healthcare disparities have a direct impact on the mental health of LGBTQ+ individuals. Limited access to appropriate care and the fear of judgment or mistreatment can deter individuals from seeking help. This can result in unaddressed mental health issues, leading to worsening symptoms and increased distress. Eliminating healthcare disparities is crucial to improve the overall mental health and well-being of LGBTQ+ individuals.
Internalized Homophobia and Biphobia
Understanding internalized oppression
Internalized homophobia and biphobia refer to the internalization of negative attitudes or beliefs about one’s own sexual orientation. LGBTQ+ individuals may internalize societal stigma and discrimination, resulting in negative self-perceptions and internalized oppression. Recognizing the presence of internalized homophobia and biphobia is essential to promote self-acceptance and combat the harmful effects of these internalized attitudes.
Negative self-attitudes and self-hatred
Internalized homophobia and biphobia can lead to negative self-attitudes and even self-hatred among LGBTQ+ individuals. The pressure to conform to societal norms and the fear of rejection can take a toll on their well-being. Building self-acceptance and fostering a positive self-image are crucial in promoting mental health and resilience.
Overcoming internalized homophobia and biphobia
Overcoming internalized homophobia and biphobia is a journey that requires support, self-reflection, and self-compassion. LGBTQ+ individuals can benefit from therapy, support groups, and engaging with affirming communities. By challenging internalized negative beliefs and embracing their true selves, individuals can begin to foster self-acceptance and experience improved mental well-being.
Bullying and Victimization
Increased risk of bullying and victimization
LGBTQ+ youth are at a higher risk of experiencing bullying and victimization. Verbal, physical, and cyberbullying based on sexual orientation or gender identity can have profound negative effects on mental health. Creating safe and inclusive environments where bullying is actively addressed and prevented is crucial in protecting the mental well-being of LGBTQ+ youth.
Effects of bullying on mental health
Bullying can have severe and long-lasting impacts on the mental health of LGBTQ+ individuals. It can lead to increased rates of anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, and substance abuse. The effects of bullying may persist into adulthood, emphasizing the importance of early intervention and comprehensive support systems.
Addressing and preventing bullying in schools and communities
Addressing and preventing bullying requires a multi-faceted approach involving schools, communities, and policymakers. Implementing anti-bullying policies, promoting inclusive education, and providing resources and support for both victims and perpetrators of bullying are essential steps towards creating safe environments for LGBTQ+ youth. Education and awareness are key in cultivating empathy and understanding among peers, fostering inclusive communities that reject bullying and discrimination.
Supportive Environments
Importance of LGBTQ+-inclusive spaces
LGBTQ+-inclusive spaces, such as schools, community centers, and healthcare settings, are crucial for the mental health and well-being of LGBTQ+ individuals. These spaces provide a sense of belonging, acceptance, and support to counteract the negative effects of discrimination and stigma. Investing in inclusive policies and practices is essential in creating environments where LGBTQ+ individuals can thrive.
Creating safe spaces in schools
Schools play a significant role in creating safe spaces for LGBTQ+ youth. Implementing anti-discrimination policies, inclusive curricula, and establishing support groups or Gay-Straight Alliances can help promote a positive school environment. Educating faculty, staff, and students about LGBTQ+ issues, fostering empathy, and addressing bullying are vital steps towards building supportive schools for all students.
Supportive counseling and therapy
Therapy and counseling provide crucial support for LGBTQ+ individuals navigating mental health challenges. Working with LGBTQ+-affirming therapists creates a safe and understanding environment where individuals can explore their identities and address mental health concerns. Cultivating cultural competence among mental health professionals is vital to ensure effective and inclusive care for LGBTQ+ individuals.
Self-Care and Resilience
Promoting self-care practices
Self-care practices are essential for maintaining mental well-being, particularly for LGBTQ+ individuals who may face unique stressors. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, self-expression, and self-compassion, such as exercise, mindfulness, and artistic pursuits, can help individuals cope with mental health challenges and build resilience.
Building resilience and coping skills
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and thrive in the face of challenges. LGBTQ+ individuals can cultivate resilience by developing coping skills, fostering healthy relationships, seeking support, and engaging in self-reflection. Resilience empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of their identity and mental health and emerge stronger and more resilient in the process.
Finding peer and community support
Peer and community support can be invaluable in the journey towards positive mental health. LGBTQ+ individuals benefit from connecting with others who share similar experiences, challenges, and victories. Support groups, community centers, and online platforms can provide a sense of belonging, validation, and mutual support.
Advocacy and Policy Changes
Advocating for LGBTQ+ rights and representation
Advocacy efforts are essential in promoting the rights and well-being of LGBTQ+ individuals. This includes fighting for legal protections against discrimination, advocating for inclusive policies in healthcare and education, and amplifying LGBTQ+ voices in media and politics. By advocating for equal rights and representation, we can create a more equitable society for all.
Importance of comprehensive sex education
Comprehensive sex education plays a vital role in promoting LGBTQ+ inclusivity. It helps dispel myths, reduce stigma, and educate individuals about sexual orientation, gender identity, and healthy relationships. Comprehensive sex education fosters understanding, acceptance, and respect for LGBTQ+ individuals, contributing to their overall mental well-being.
Policy changes to improve mental health support for LGBTQ+ youth
Policy changes are necessary to improve mental health support for LGBTQ+ youth. This includes increasing funding for LGBTQ+-specific mental health services, training healthcare providers on LGBTQ+ cultural competence, and implementing anti-discrimination policies in schools and workplaces. By advocating for policy changes, we can ensure that LGBTQ+ youth receive the support and resources they need to thrive.
In conclusion, understanding LGBTQ+ identities is a crucial step towards creating a more inclusive and supportive society. By exploring sexual orientation and gender identity, we can foster acceptance and respect for diverse experiences. Mental health disparities, the coming out process, intersectionality, and healthcare disparities all play significant roles in the lives of LGBTQ+ individuals. Addressing internalized homophobia and biphobia, bullying and victimization, and fostering supportive environments are vital in promoting positive mental health outcomes. Self-care, resilience, and advocacy efforts are essential in empowering LGBTQ+ individuals and creating a more equitable future. Let us actively work towards creating a society where every individual can embrace their LGBTQ+ identity with pride and without fear of discrimination or stigma.