Mental Health In The Face Of Multiple Sclerosis
Living with multiple sclerosis (MS) can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. In this article, we will explore the impact of MS on mental health and discuss strategies to maintain a positive mindset in the face of this chronic illness. Whether you are personally affected by MS or know someone who is, it is crucial to understand the importance of addressing mental health alongside physical symptoms. So, let’s dive into the world of MS and discover ways to nurture your mental well-being throughout the journey.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
Definition and Overview of Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin. This damage disrupts the communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms and impairments. MS can vary greatly in severity and progression, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may become severely disabled.
Causes and Risk Factors of Multiple Sclerosis
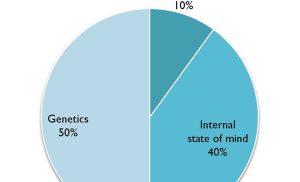
The exact cause of MS is still unknown, but researchers believe it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic predisposition plays a role, as individuals with a family history of MS have a slightly higher risk of developing the condition. Certain environmental factors, such as vitamin D deficiency, smoking, and infections, have also been associated with an increased risk of MS. However, it’s important to note that having these risk factors does not guarantee the development of MS.
Symptoms and Progression of Multiple Sclerosis
The symptoms of MS can vary widely depending on the location and extent of nerve damage. Common symptoms include fatigue, difficulty walking, muscle weakness or spasms, numbness or tingling in the limbs, problems with coordination and balance, and bladder or bowel dysfunction. As the disease progresses, some individuals may experience cognitive impairment, emotional changes, and even difficulties with speech and swallowing. The progression of MS is unpredictable and can be relapsing-remitting, where symptoms come and go, or progressive, where symptoms gradually worsen over time.
Impact of Multiple Sclerosis on Mental Health
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Individuals living with MS often face significant challenges that can have a profound impact on their mental health. Research indicates that rates of mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are higher among MS patients compared to the general population. According to a study published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, depression affects approximately 50% of people with MS at some point during their lives. Similarly, anxiety disorders are also common, with about 20-40% of MS patients experiencing symptoms of anxiety.
Psychological Impact of Multiple Sclerosis
The psychological impact of MS goes beyond the physical symptoms of the disease. The unpredictable nature of MS can lead to feelings of uncertainty and loss of control, which can contribute to heightened levels of stress, frustration, and even grief. Additionally, the physical limitations caused by MS, such as mobility issues or chronic pain, can lead to increased levels of psychological distress. Coping with the challenges and uncertainties of MS can be emotionally draining and may impede an individual’s quality of life.
Cognitive Impairment and Emotional Changes in Multiple Sclerosis
In addition to the physical and psychological symptoms, MS can also cause cognitive impairment and emotional changes. Cognitive deficits can include difficulties with memory, attention, problem-solving, and processing speed. These cognitive impairments can significantly impact daily functioning and overall quality of life. Emotional changes, such as mood swings, irritability, and emotional lability, are also common in MS patients. These emotional fluctuations can be challenging to cope with and can affect personal relationships and social interactions.
Psychiatric Disorders Associated with Multiple Sclerosis
Depression in Multiple Sclerosis
Depression is one of the most prevalent psychiatric disorders associated with MS. The constant challenges and limitations imposed by the disease can significantly contribute to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of depression in MS patients and seek appropriate support and treatment. Treatment options for depression in MS may include a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Anxiety Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis
Anxiety disorders are also common in individuals living with MS. The uncertainties surrounding the progression of the disease, the fear of experiencing relapses or worsening symptoms, and the impact of MS on daily life can all contribute to heightened levels of anxiety. Symptoms of anxiety may include excessive worrying, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and physical manifestations such as heart palpitations or panic attacks. Treatment for anxiety disorders may involve therapy, medication, and various relaxation techniques.
Bipolar Disorder and Multiple Sclerosis
Although less common than depression and anxiety, individuals with MS may also experience symptoms of bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder is characterized by extreme mood swings, fluctuating between periods of depression and periods of mania or hypomania. MS can complicate the diagnosis and management of bipolar disorder, as some symptoms may overlap with the physical and emotional manifestations of MS. A comprehensive treatment approach involving medication, therapy, and support is crucial for individuals with co-occurring bipolar disorder and MS.
Diagnosing and Treating Mental Health Conditions in Multiple Sclerosis
Challenges in Diagnosing Mental Health Conditions in Multiple Sclerosis
Diagnosing mental health conditions in individuals with MS can be challenging. Many of the symptoms of mental health disorders, such as depression or cognitive impairment, can overlap with the physical manifestations of MS. This overlap often leads to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of mental health issues in MS patients. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in assessing the mental well-being of individuals with MS and consider mental health screenings as part of routine care.
Screening and Assessment of Mental Health in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Screening and assessing the mental health of individuals with MS is crucial for early detection and intervention. Healthcare providers may use standardized tools and questionnaires to assess symptoms of depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment in MS patients. Additionally, a comprehensive evaluation should include a thorough medical history, evaluation of the patient’s social support system, and consideration of any other factors that may contribute to the individual’s mental well-being. Collaborative efforts between neurologists and mental health professionals are essential in providing holistic care for MS patients.
Psychotherapy and Counseling for Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Psychotherapy and counseling play a vital role in the treatment of mental health conditions in MS patients. Various therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals develop coping strategies, manage symptoms, and improve overall well-being. Therapy can also provide a safe space for individuals to express their emotions, adapt to life with MS, and explore strategies for maintaining a positive outlook. Furthermore, family and caregiver involvement in therapy can enhance support systems and improve the overall mental health of individuals with MS.
Managing Mental Health in Multiple Sclerosis
Self-Care and Lifestyle Changes
Self-care and lifestyle changes can significantly impact the mental well-being of individuals with MS. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, stress reduction, and emotional well-being can help manage the psychological impact of living with a chronic illness. This may include practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies or creative outlets, and maintaining a healthy balance between work, rest, and leisure activities. Taking care of one’s physical health, such as engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a nutritious diet, can also indirectly improve mental well-being in individuals with MS.
Medication and Pharmacological Treatment
Medication can be an essential component of managing mental health conditions in individuals with MS. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. In some cases, mood stabilizers or antipsychotic medications may be necessary to manage more severe psychiatric symptoms. However, it is vital to work closely with healthcare providers to find the right balance of medication and monitor any potential side effects.
Supportive Therapies and Alternative Approaches
In addition to medication and therapy, individuals with MS may benefit from supportive therapies and alternative approaches to manage their mental health. Supportive therapies, such as support groups or peer counseling, provide an opportunity to connect with others who understand the challenges of living with MS. Additionally, complementary and alternative therapies, including acupuncture, yoga, and meditation, may help reduce stress, improve overall well-being, and enhance coping skills. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating alternative approaches into treatment plans.
Importance of Support Systems
Building a Strong Support Network
Building a strong support network is crucial for individuals with MS to navigate the challenges they may face. Support can come from family, friends, healthcare professionals, and even online communities dedicated to supporting individuals with MS. Connecting with others who understand the unique aspects of living with MS can help reduce feelings of isolation, provide validation, and offer practical advice for managing the disease. A strong support network can provide emotional support, offer a listening ear, and assist in accessing appropriate resources and services.
Psychoeducation for Patients and Their Families
Psychoeducation plays a vital role in empowering individuals with MS and their families to better understand the disease and its impact on mental health. Education about the disease process, treatment options, symptom management, and available support services can equip individuals and their loved ones with the knowledge they need to navigate the challenges that may arise. Psychoeducation can also help reduce stigma surrounding mental health and promote open communication within the family unit.
Support Groups and Peer Support
Joining support groups or engaging in peer support activities can provide individuals with MS a sense of belonging and an opportunity to share experiences with others who are facing similar challenges. Support groups can be in-person or online, and they provide a platform to express emotions, receive guidance, and learn from others’ coping strategies. Peer support can be a valuable source of validation, encouragement, and inspiration in managing the mental health impact of MS.
Revitalizing Mental Health through Physical Activity
Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health in Multiple Sclerosis
Physical activity and exercise have been shown to have numerous benefits on mental health in individuals with MS. Regular exercise can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, improve mood and self-esteem, boost cognitive function, and enhance overall well-being. Engaging in exercise also promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers. Additionally, exercise can enhance physical fitness, which can lead to increased independence and improved quality of life for individuals with MS.
Types of Exercise for Multiple Sclerosis Patients
When it comes to exercise for individuals with MS, it’s crucial to consider individual abilities, preferences, and any limitations imposed by the disease. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and yoga can be beneficial as they minimize strain on the joints and muscles. Aerobic exercises, strength training, and balance exercises can also be incorporated into exercise routines to target specific physical and mental health benefits. Working with healthcare providers or physical therapists can help determine the most appropriate exercise program tailored to an individual’s needs.
Adapting Exercise to Individual Abilities
Adapting exercise to individual abilities is key for individuals with MS to engage in physical activity safely and effectively. Fatigue, muscle weakness, and mobility limitations may require modifications to exercise routines. This may involve shorter workout durations, using assistive devices, or selecting exercises that can be done in a seated or lying position. Working with healthcare professionals or physical therapists experienced in MS can provide essential guidance on adapting exercises to accommodate specific needs and abilities.
Nutrition and its Impact on Mental Well-being
The Gut-Brain Connection in Multiple Sclerosis
Emerging research suggests that there is a complex relationship between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain connection. The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of microorganisms living in the intestines, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including mental health. Disruptions in the gut microbiome, such as changes in the diversity and balance of gut bacteria, have been linked to an increased risk of mental health disorders. The gut-brain connection in MS is an area of active research, and adopting a gut-healthy diet may have potential benefits for mental well-being.
Dietary Recommendations for Mental Health in Multiple Sclerosis
While there is no specific diet that guarantees mental health improvements in individuals with MS, adopting a well-balanced and nutritious diet is beneficial for overall well-being. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients for optimal brain function. Additionally, some evidence suggests that certain dietary approaches, such as the Mediterranean diet or the anti-inflammatory diet, may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, which can have positive effects on mental health.
Supplements and Vitamins for Mental Well-being
In some cases, individuals with MS may benefit from certain supplements and vitamins for supporting mental well-being. Vitamin D supplementation, for example, is commonly recommended for individuals with MS due to its potential immune-modulating effects and its association with improved mood. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil or flaxseed oil, may also have potential benefits for mental health. However, it is essential to consult with healthcare providers before starting any new supplements, as individual needs and potential interactions with medications should be considered.
Coping with Uncertainty and Emotional Challenges
Acceptance and Adaptation to the Disease
Coping with the uncertainty and emotional challenges that arise with MS requires acceptance and adaptation to the disease. Accepting the diagnosis and the limitations imposed by the disease can be a difficult process, but it is an essential step towards finding resilience and managing emotional well-being. Embracing a new outlook on life, setting realistic expectations, and focusing on what is within one’s control can help individuals with MS navigate the emotional challenges they may encounter.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Emotional Management
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used therapeutic approach for individuals with MS who are struggling with emotional management. CBT aims to identify and modify negative thoughts and behavioral patterns that contribute to emotional distress. By learning effective coping strategies and problem-solving techniques, individuals can develop healthier ways of managing stress, anxiety, and depression. CBT provides practical tools and skills that can be applied in everyday life, helping individuals build resilience and improve their overall mental well-being.
Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
Mindfulness and meditation practices have been shown to have numerous benefits for individuals with MS in managing emotional challenges. Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment with an attitude of openness and non-judgment. Meditation practices, such as focused breathing or body scan meditations, can help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and enhance emotional well-being. Engaging in regular mindfulness and meditation practices can cultivate a sense of inner calm and provide individuals with MS with a valuable tool for managing emotional ups and downs.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Maintaining Social Connections and Relationships
Maintaining social connections and relationships is vital for enhancing the quality of life of individuals with MS. The challenges imposed by the disease can sometimes lead to social isolation, which can further exacerbate mental health issues. Actively seeking and nurturing relationships with family, friends, and support networks can provide emotional support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and foster a sense of belonging. Social activities, such as joining clubs or engaging in community events, can also offer opportunities for social interaction and overall well-being.
Finding Purpose and Meaning in Life
Finding purpose and meaning in life can significantly impact the mental well-being of individuals with MS. Engaging in activities that align with personal values and interests, such as volunteering or pursuing a hobby, can provide a sense of accomplishment, fulfillment, and overall life satisfaction. Adjusting goals and aspirations to accommodate the limitations imposed by the disease can help individuals maintain a sense of purpose and continue to lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges they face.
Exploring Creative Outlets and Hobbies
Engaging in creative outlets and hobbies can be a source of joy, self-expression, and stress relief for individuals with MS. Art, music, writing, or other creative activities provide an opportunity to channel emotions, explore individual talents, and focus on the present moment. Creative outlets can serve as a form of therapy, allowing individuals to express their thoughts and emotions, increase self-awareness, and find solace in their creative endeavors. Exploring various hobbies and creative outlets can bring renewed energy and a sense of purpose to life with MS.